Home > Conditions Treated > Osteoarthritis
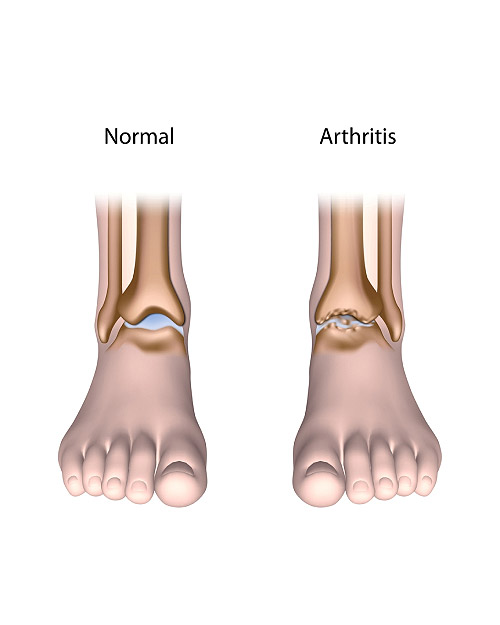
It affects millions of people worldwide. It is a degenerative disease that gradually wears down the protective cartilage that cushions the ends of your bones. Osteoarthritis can affect any joint in the body. However, the disorder most often affects the joints in the hands, knees, hips, ankles and spine.
Among the conditions that are associated with osteoarthritis are the following: Aging, Joint Injury, Joint Misalignment/Dislocation, Repetitive Overuse, Hereditary Factors/Collagen Defects, Obesity, Disease sequela (e.g. Gout, Psoriasis, Sjogren’s Disease, Lupus, Ankylosing Spondylitis, Lyme Disease, Scleroderma, etc), Bone Deformities, Metabolic Diseases (Diabetes, Hemochromatosis).
Medical history, a physical examination, imaging and lab tests help to make an OA diagnosis. Joint aspiration done under local anesthetic may help rule out other causes of similar joint problems. Joint aspiration is a procedure which uses a small needle to remove a sample of joint fluid. This test will look for infection or crystals in the fluid which can rule out other medical conditions or other forms of arthritis. X-rays can show joint or bone damage or changes related to osteoarthritis. Local anesthetic diagnostic injections can also be done to confirm the diagnosis and help with treatment planning. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) gives a better view of cartilage and other parts of the joint.
At-home treatments can include: Daily exercise (walking, yoga, aqua classes), Weight Loss, Adequate Sleep, Heat and Cold therapy, Topical Analgesics, Acetominophen. Natural remedies such as fish oil, green tea, ginger, glucosamine/chondroitin sulfate can also be helpful. A high-quality diet may help provide relief from OA symptoms by reducing inflammation and swelling. Eating foods high in the following anti-inflammatory vitamins and nutrients can be highly beneficial such as vitamins C & D, beta-carotene, Omega-3 fatty acids. Increasing your intake of foods with anti-inflammatory properties will help, too. These practices can help take the edge off of your symptoms and improve your quality of life.
Your provider may also be able to prescribe oral or topical pain or anti-inflammatory medications. Hyaluronic acid can be injected into the joint to increase lubrication to temporarily reduce symptoms. Physical Therapy may be prescribed to reduce pain, increase balance, strengthen muscle that surrounds affected joints and to increase range of motion limitations. Splints and braces can also be prescribed to reduce strain to affected joints.



While cartilage is very beneficial to the body, it doesn’t heal itself as well as most other tissues. Cartilage cells (chondrocytes) do not often replicate or repair themselves, which means damaged or injured cartilage will not likely heal well without medical intervention.
Orthobiologic Treatments may provide and excellent alternative to help deal with foot and ankle osteoarthritis. The aim of using these treatments is to support your body’s self-healing processes, reverse disease progression and suppress inflammatory reactions that can worsen pain, leading to symptom relief and recovery of function.
As part of a cell-based treatment, regenerative cells can be collected from bone marrow and blood with minimal discomfort. These cells can then be processed in a state-of-the-art laboratory utilizing the latest technology. Finally, the regenerative cells, in combination with natural growth and healing factors, can be injected where they are needed – such as an inflamed hip or knee joint. Over time, the cells can potentially repair and regenerate the damaged tissues, resulting in relief of pain and improvement in mobility and function.
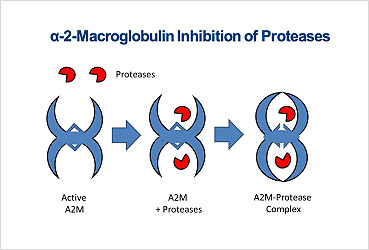
In addition, Alpha-2-Macroglobulin (A2M) can be used to prevent cartilage breakdown in patients, promote tissue growth and support the overall restoration of an affected joint. A2M inhibits the breakdown of cartilage and shuts down the destructive inflammatory proteins in the joint. A2M can prevent and minimize ongoing osteoarthritis.
In very severe cases, surgical options are available to address cartilage degeneration/injury. Among these are: Arthroscopic Debridement, Microfracture surgery, Osteoarticular Transfer System (O.A.T.S) procedure, Arthroplasty (jt removal), Arthrodesis (Joint fusion) or Partial/Total Joint Replacement.
Although Orthobiologic Cell Therapy is considered by some people to be experimental, various research studies show that some marrow aspirate concentrate and platelet rich plasma injections may provide excellent relief from joint and musculoskeletal pain and ongoing inflammation.
600 Worcester Rd, Ste 301,
Framingham, MA 01702
This information is for educational purposes only and is NOT intended to replace the care or advice given by your physician. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider before starting any new treatment or with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. For more information see our Medical Disclaimer.